On-Page SEO Checklist - Optimize your Website
In the realm of search engine optimization (SEO), on-page optimization plays a vital role in enhancing the visibility and ranking of your website in search results. By optimizing the structure, content, and various elements of your web pages, you can increase their relevance and appeal to both users and search engines. This On-Page SEO Checklist serves as a comprehensive guide to help you effectively optimize your website.
The checklist covers various aspects of on-page SEO, including keyword usage, heading tags, internal and external links, title tags, meta descriptions, URL addresses, image optimization, and user experience. Each of these elements plays a significant role in determining your website's performance in search engine rankings. By following this checklist, you can ensure that your website aligns with current SEO best practices, giving it a better chance of ranking well in search results.
Remember, high-quality content remains the cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy. While implementing on-page SEO techniques is crucial, it is equally important to create valuable, informative, and engaging content that caters to the needs of your target audience. By providing valuable content and optimizing your web pages using the checklist, you can significantly improve your chances of achieving successful SEO results.
What is an On-Page SEO Checklist?
An On-Page SEO Checklist involves optimizing the structure and content of a website for search engines. This process includes optimizing the text, title tags, internal links, and meta descriptions on site pages.
In addition to link building and technical SEO activities (which will be discussed in the following guides), on-page SEO is crucial for achieving a high ranking in search results.
In this On-Page SEO Checklist, you will learn:
- How to optimize the text on your pages.
- How to write title tags and meta descriptions to improve your ranking.
- How user experience impacts your ranking and what you can do about it.
Note: If you are still unsure about the keywords your target audience is using to find your website, read 'How to Do Keyword Research for SEO.' Understanding the keywords you want to target is essential for on-page optimization."
Why do you need On-Page SEO Checklist?
Content is the most crucial factor in your SEO strategy. Your SEO results will fail if your content is of poor quality and fails to provide value to users.
Search engines increasingly prefer comprehensive content that thoroughly covers the topic and solves users' problems. The average length of text on pages ranking on the first page of Google is continuously increasing, typically ranging between 1500-2000 words per page, unless it pertains to a less popular topic or a less competitive industry.
Regardless of your industry, having a blog on your website is essential for achieving significant SEO results. It is necessary to write blog posts that comprehensively cover the topic, based on sufficient interest, which can be determined through keyword research.
Now, let's delve into the On-Page SEO Checklist and explore the key aspects to focus on:
- Use of keywords in the text
- Heading tags checklist
- Internal links checklist
- Title tags checklist
- Meta description checklist
- URL address checklist
- Image optimization checklist
- External links checklist
- User experience checklist
Before we proceed to the On-Page SEO Checklist, there are a few things you should avoid doing.
How not to do on-page SEO
Google continues to evolve and become more sophisticated. In the past, simply cramming a large number of keywords onto the pages of your website and acquiring low-quality backlinks would guarantee a high ranking on search engines for those targeted keywords.
However, that approach no longer works. Google's algorithm now penalizes websites that engage in such undesirable practices, as they do not reflect the true quality of the site and its content.
This may seem strict, but the reason behind it is simple: Google aims to provide users with relevant content that answers their questions and solves their problems. Of course, Google's motivation is not purely altruistic; they also benefit financially through advertising revenue.
Additionally, it is crucial for SEO that the content you publish on your site is original. This not only helps you avoid potential legal issues but also ensures that Google ranks your page well in search results. Even if you find someone else's content interesting for your users, Google will not prioritize that page in terms of search ranking.
When it comes to on-page SEO, everything we discuss below should be approached with a focus on enhancing the user experience. Avoid excessive use of internal links and keywords, as such practices will not yield SEO benefits.
Now that you understand the negative impact of questionable SEO techniques on optimization, let's proceed to the On-Page Checklist and explore how to optimize your content.
Use of keywords in the text
I mentioned earlier that you shouldn't excessively use keywords in the content text, but that doesn't mean you shouldn't use them at all. Each page and text on the website should be optimized around a specific keyword or phrase.
However, it's important to note that using the keyword too frequently is not recommended. Ideally, you should aim to use a keyword every 200-300 words of text.
In addition, it is crucial to include the keyword at least once within the first 100-150 words since Google assigns more significance to the text at the beginning of the page.
For instance, if you want to rank for the keyword 'Top 8 Dog Breeds,' your introductory 100-150 words could be:
'We have delved into the topic of dog lifespans and will now provide a detailed overview of the Top 8 Dog Breeds that are known to have the longest lifespan.'
To analyze your writing, you can utilize a tool called 'Analyze My Writing.' This tool allows you to determine the frequency of a specific term used in your content. Choose the 'Common Words and Phrases' option and click on 'Analyze Text.' This tool also offers other useful options, such as readability analysis and identifying the use of passive voice in the text.
If you are starting to optimize your site, it is recommended to focus on incorporating 'long-tail' keywords in your text. These are phrases that may not have a high search volume per month, but they also face less competition in terms of ranking. This increases your chances of appearing on the first page of search results for those particular phrases.
Heading tags Checklist
Heading tags are snippets of code that assist search engines in comprehending the content of a website. The H1 tag represents the main title of the page, while H2 denotes the subtitle. H3, on the other hand, functions as a subheading within H2, and so forth.
This hierarchical structure of titles facilitates the indexing process for search engines, as it enables them to grasp the page's topic based on the organization of its content.
Typically, the text within the H1 tag serves as the page title, although there may be exceptions. To verify if a page has an H1 tag, you can right-click anywhere on the page and select "View Page Source."
A new window will open, displaying the HTML code of the page. Look for an H1 tag that might resemble the following:
<h1 class="entry-title">Title</h1>
When optimizing a page, it is recommended to include a single H1 tag that contains the targeted keyword. Depending on the text's length, adding additional H2 tags is advisable, with one or two of them incorporating the keyword.
For instance:
<h2 style="text-align: center;">Subheading 1</h2>
<h2 style="text-align: center;">Subheading 2</h2>
If you are optimizing your website using Blogger or WordPress, the page title will automatically be assigned the H1 tag. Adjusting H2, H3, and subsequent titles can be easily done through the Blogger panel. Simply highlight the text and select the desired Heading tag.
Internal links Checklist
Internal links are links that lead from one page of a site to another page within the same site and are considered crucial factors for on-page SEO.
It is important to distinguish between navigational and contextual internal links.
Navigational internal links refer to links present in the main menu, footer, and other navigation elements.
Contextual internal links, on the other hand, are links embedded within the content of a page. These contextual links are of particular interest because search engines assign greater importance to them, while navigational links hold less significance.
While internal links themselves may not directly provide SEO benefits, they play a crucial role in helping Google discover and index multiple pages of a website, thereby contributing to long-term ranking improvements.
To make the most of internal links, it is advisable to link to well-ranked pages on your site from the pages you wish to enhance in terms of ranking.
The anchor text (the clickable text of a link) should ideally contain the keyword you want the linked page to rank for.
For instance, in the beginning of this On-Page SEO Checklist, I included a link with the anchor text "How to Do Keyword Research for SEO," which directs users to a guide on the same topic.
Similar to keywords, internal links should be used judiciously and only where they are relevant and helpful to users.
Title tag Checklist
- Add a keyword: The title tag should contain the keyword you want the page to rank for. It's even better if you can place it at the beginning of the title tag while ensuring the title remains meaningful.
- Optimize the length: Ideally, the title tag should be between 45 and 55 characters long. Otherwise, search engines will truncate it with "...". If you can't shorten the title text, slightly exceeding the character limit is acceptable. However, keep in mind that this might reduce your clickthrough rate (CTR) even though it won't have a significant impact on SEO.
- Mention your brand: If there's still space available in the title tag, a great way to utilize it is by mentioning your brand at the end. Best practice suggests using a "|" or "-" to separate the brand name. This will enhance the clarity of your title tags.
<head><title>Enter the title tag of the page here</title></head>
Meta description Checklist
Title tags and Meta descriptions are HTML elements that describe the content of a webpage. The Meta description is the brief summary of the page that appears on search engine results.
Each page on your website should have a unique Meta description. It serves to describe the content of the page and provides a summary of what users can expect to find.
Adding a keyword to the Meta description will not directly impact your search engine rankings. However, it can potentially increase the organic clickthrough rate, which is one of the factors Google considers in terms of user experience and ranking. Google also highlights the words in the Meta description that match the search query.
The length of a Meta description should ideally be limited to a maximum of 150 characters.
If your website is not built on platforms like Blogger or WordPress, the HTML implementation would look something like this:
<head>
<meta name="description" content="Enter the text of the Meta description here." />
</head>
URL address Checklist
URLs are the addresses of individual content on the Internet. Search engines display URLs in search results, so the naming and formatting of URLs can impact the number of clicks you receive. Users rely on URLs to determine which websites to click on, while search engines use them to rate and rank pages.
Optimizing a page URL is quite simple. The URL should meet the following criteria:
- It should contain a relevant keyword.
- It shouldn't be excessively long, both for browser compatibility and user experience.
- If your page address consists of multiple words, separate them with hyphens (-). Some web browsers may not interpret your URL correctly if you use underscores (_) or combine the words.
Furthermore, it is important for the URL structure of your site to be logical.
For instance, which of the following two URLs is clearer to you?
seobloggertips.com/2021/12/what-is-seo-and-why-do-you-need-it
or
seobloggertips.com/2021/12/seo?=need-42158
URL optimization alone will not improve your ranking as significantly as the other techniques listed in this guide. However, when combined with those techniques and a better user experience, it can greatly enhance your position in search results.
Image optimization for On-Page SEO Checklist
In order to optimize the images on your site for search engines and users, it is important to provide a name and alt text (alternative text) for each image that accurately describes its content.
You can incorporate relevant keywords into the image name and alt text, but only if they are contextually appropriate for the image.
The alt text serves the purpose of informing search engines about the image content, enabling them to better understand the context of the entire page and rank your image in search results. Moreover, it assists visually impaired users by providing a description of the image when they use screen readers.
In Blogger, you can easily modify the image name and alt text by clicking on the image.
Alternatively, you can input the title and alt text of the image through HTML:
<img title="Enter image name here" alt="Enter alternative image text here" />
External links Checklist
External links are links that lead from your site to another site. While it may sound strange, linking to other relevant and high-quality sites can actually benefit your SEO.
There are a few things to keep in mind regarding external linking in order to reap on-page SEO benefits.
Firstly, make sure to exclusively link to quality sites that are useful to your audience and that also link back to your content. Avoid suspicious sites that publish spam content and include irrelevant links.
Secondly, it's important not to overdo external linking. Include a link where it naturally fits and provides users with a valuable source of information.
Lastly, remember to set external links to open in a new tab. The time spent on your site is one of the factors considered by search engines for SEO, so you don't want users to leave your site in the middle of reading your content.
User experience Checklist
User experience is an increasingly significant SEO factor, which continues to gain importance with every new update of the Google algorithm.
Several factors contribute to user experience, such as color, site structure, text size, and the positioning of specific elements on the page. However, we will delve into these topics in more detail at another time. For now, let's concentrate on the SEO factors that have the greatest impact on rankings.
Organic CTR clickthrough rate
Organic clickthrough rate (CTR) is the ratio of users who click on your link in the search results to the total number of users who only saw the link but did not click.
When a large number of users click on your link in the search results and visit your page, it sends a signal to search engines that your site is relevant to that particular search term.
Several factors can influence the clickthrough rate, including:
- Title tags
- Meta description
- Position on the search results page
In an earlier section, we discussed the importance of optimizing your title tags and meta descriptions for both search engines and organic clickthrough rates.
Your current position in the search results significantly impacts your clickthrough rate. Users are more likely to click on higher-ranking results unless they are satisfied with the current results and need to continue searching for the information they require.
If the rate of organic clicks for a specific result consistently surpasses the click rate for higher-ranked results, search engines will eventually boost the position of the link with the higher clickthrough rate.
You can access the organic clickthrough rate data on the Google Search Console platform under the "Performance" section."
You can observe the average organic click-through rate (CTR) for all pages here. Additionally, by clicking on individual pages, you can access the specific organic CTR for each page.
Average Time On Page - Google Analytics
Search engines calculate the time users spend on a site, especially if those users arrived through organic search.
To maximize the duration of user engagement, it is crucial to immediately capture their interest and sustain their attention. Insufficient information or poorly organized content will quickly disengage users, causing them to leave.
Optimize content readability and minimize reading fatigue by utilizing short paragraphs and incorporating ample visual elements, such as pictures. Additionally, ensure legible fonts with a minimum size of 14-15.
Consider including relevant video content on pages, if available, as it enhances the average time users spend on the site. Users tend to continue watching videos, thereby increasing their overall engagement.
In Google Analytics, you can track the duration of user visits on specific pages by accessing the 'Behavior Overview' and viewing the 'Average time on page' metric.
The ideal average time users spend on your site would be over 3 minutes so try to strive for that.
Bounce Rate
The one-page visit rate refers to the percentage of visitors who leave a website without taking any action, such as clicking on a link to another page, filling out a contact form, or making a purchase. The primary objective is to minimize the bounce rate, indicating visitor engagement.
This metric informs search engines about user satisfaction with your site.
However, it's important to note that if users only visit one page and then leave, it doesn't necessarily imply dissatisfaction with the content. They may have found what they were seeking and didn't require further exploration. Nonetheless, it's still beneficial to encourage them to take action.
For instance, if it's a blog, you can include links to related articles alongside or within the text. This allows users who are interested in similar information to click on these links instead of returning to search results and searching for another site.
Another effective strategy is to incorporate an exit popup, triggered when someone attempts to leave the site. When implemented correctly, it doesn't have to be intrusive or diminish the user's experience.
To monitor the bounce rate, you can utilize Google Analytics by navigating to the Behavior > Overview > Bounce Rate section.
Try to lower this percentage below 40%
Page Speed
The loading speed of the site does not directly affect SEO, but it does have an impact on other factors related to user experience, as we have listed so far.
Modern users have little patience for websites that take a long time to load. If your site takes more than a few seconds to load, visitors are likely to abandon it and return to the search results to click on another site.
I recommend two tools to check the speed of your site:
In my experience, Pingdom is the most accurate tool for measuring specific
load times. However, it has a limitation in terms of the number of regions
available for testing the speed. Nevertheless, these regions will usually be
sufficient for you to get a rough idea of the speed and receive a few
suggestions on how to optimize your site for faster loading.
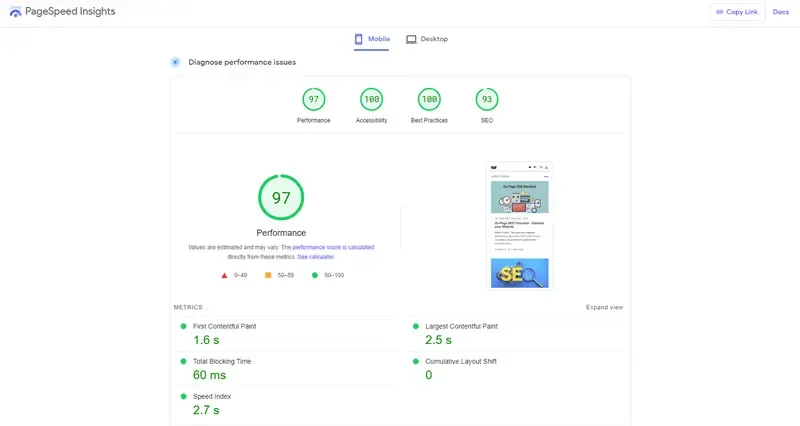
While Google Speed Insights may not provide an exact measurement of your upload speed, it can give you a general speed rating and provide numerous suggestions to enhance the speed of your website.
More importantly, this tool also provides data on download speeds for mobile devices. Since the majority of users access the site via mobile phones, it is crucial to optimize the download speed of the mobile version as well.
To enhance user experience and minimize frustration, it is crucial to optimize the website's load speed to less than 3 seconds on all devices. Anything beyond this threshold can potentially lead to user frustration and abandonment of the site.
Conclusion
On-page SEO is an integral part of optimizing your website for search engines. By following the On-Page SEO Checklist outlined in this guide, you can enhance the structure, content, and user experience of your website, leading to improved visibility and higher rankings in search results.
Remember to strategically use keywords throughout your content without overstuffing them. Utilize heading tags to organize your content and make it more comprehensible for search engines. Implement internal and external links to enhance the crawlability and authority of your website. Optimize your title tags and meta descriptions to attract users and improve clickthrough rates. Pay attention to the URL addresses of your web pages, ensuring they are concise and descriptive. Additionally, don't forget to optimize your images with appropriate names and alt text.
Lastly, prioritize user experience by creating a visually appealing website that is easy to navigate and provides valuable information to your visitors. A positive user experience can lead to higher organic clickthrough rates, ultimately boosting your website's ranking in search results.
By implementing these on-page SEO techniques and consistently providing high-quality content, you can improve your website's visibility, attract more organic traffic, and achieve higher search engine rankings. Keep this checklist handy as you optimize your website and stay up to date with the ever-evolving world of SEO.
Editor's Note: This post was originally published in December 2021 and has been completely revamped and updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.